
Certain social, demographic, and treatment variables seem to contribute to these poor outcomes. Multivariate analyses revealed that presence of two or more comorbidities, being married, having an annual personal income of less than 25,000 US dollars, not having attained a high-school diploma, and having been treated with external fixation with or without limited internal fixation were significantly related to poorer results as reflected by at least two of the five primary outcome measures.Īt more than three years after the injury, pilon fractures can have persistent and devastating consequences on patients' health and well-being. Of sixty-five participants who had been employed before the injury, twenty-eight (43%) were not employed at the time of follow-up nineteen (68%) of the twenty-eight reported that the pilon fracture prevented them from working. Thirty-five percent of the patients reported substantial ankle stiffness 29%, persistent swelling and 33%, ongoing pain. General health, as measured with the Short Form-36 (SF-36), was significantly poorer than age and gender-matched norms. Our team of physicians are committed to finding you the best treatment for your fracture pain that suits your individual needs. A secondary outcome measure was employment status.Įighty (78%) of 103 eligible patients were evaluated at a mean of 3.2 years after injury. The primary outcomes that were measured included general health, walking ability, limitation of range of motion, pain, and stair-climbing ability. By Krystyna 1.37K subscribers Subscribe 109 Share 5.8K views 4 years ago After 8 months of recovery from pilon fracture type 3, I was able to run again. Study participants returned to the initial treatment centers for a comprehensive evaluation of their health status. Patient, injury, and treatment characteristics were recorded from patient interviews and medical record abstraction. Our purpose was to assess midterm health, function, and impairment after pilon fractures and to examine patient, injury, and treatment characteristics that influence outcome.Ī retrospective cohort analysis of pilon fractures treated at two centers between 19 was conducted. Physical therapy will be recommended following surgery.Although a number of investigators have documented clinical outcomes and complications associated with tibial plafond, or pilon, fractures, very few have examined functional and general health outcomes associated with these fractures. Surgery may also be performed if the inflammation is associated with a tear that can be repaired. If the tendon or tendons are being irritated by surrounding tissue, surgery may be performed to release the tendon. Surgery is rarely necessary for tendonitis.

A physical examination will be performed during which the ankle is manipulated, and mobility and pain is assessed. At more than three years after the injury, pilon fractures can have persistent and devastating consequences on patients health and well-being. Your doctor will review your medical history and discuss your activities. Pain on rolling the foot inward or outward.
Pain behind the ankle which increases with activities.Peroneal tendonitis is associated with:.
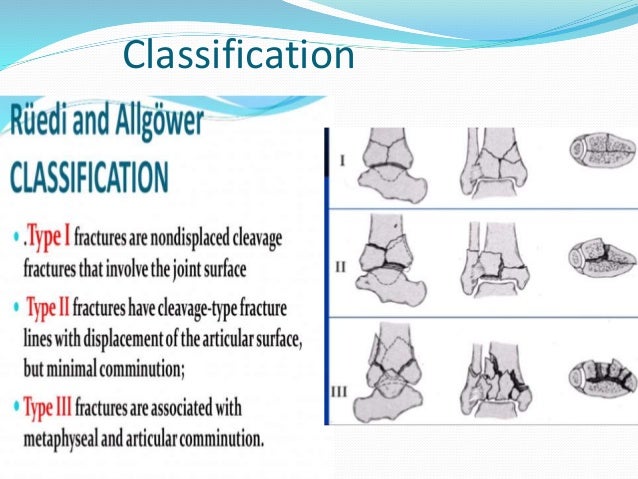
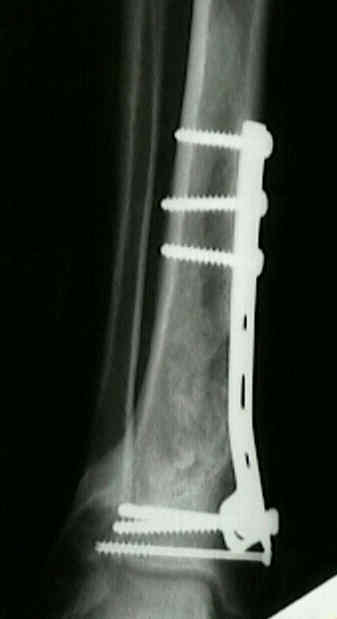
The tendons gradually thicken to accommodate the increase in activity and load but are likely to develop scar tissue making them vulnerable to tears.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
